RAID Data Recovery
At WeRecoverData.com® RAID Data Recovery is one of our specialties in the array of data recovery services we offer . RAID is a great system for increasing speed and availability of data as it offers considerably more data protection than non-RAID disk systems. However, its management of the disks and the data distribution across them can be extremely complex. (Learn more about RAID)
See also: Snap Server Data Recovery and Apple Xserve / Xsan Data Recovery
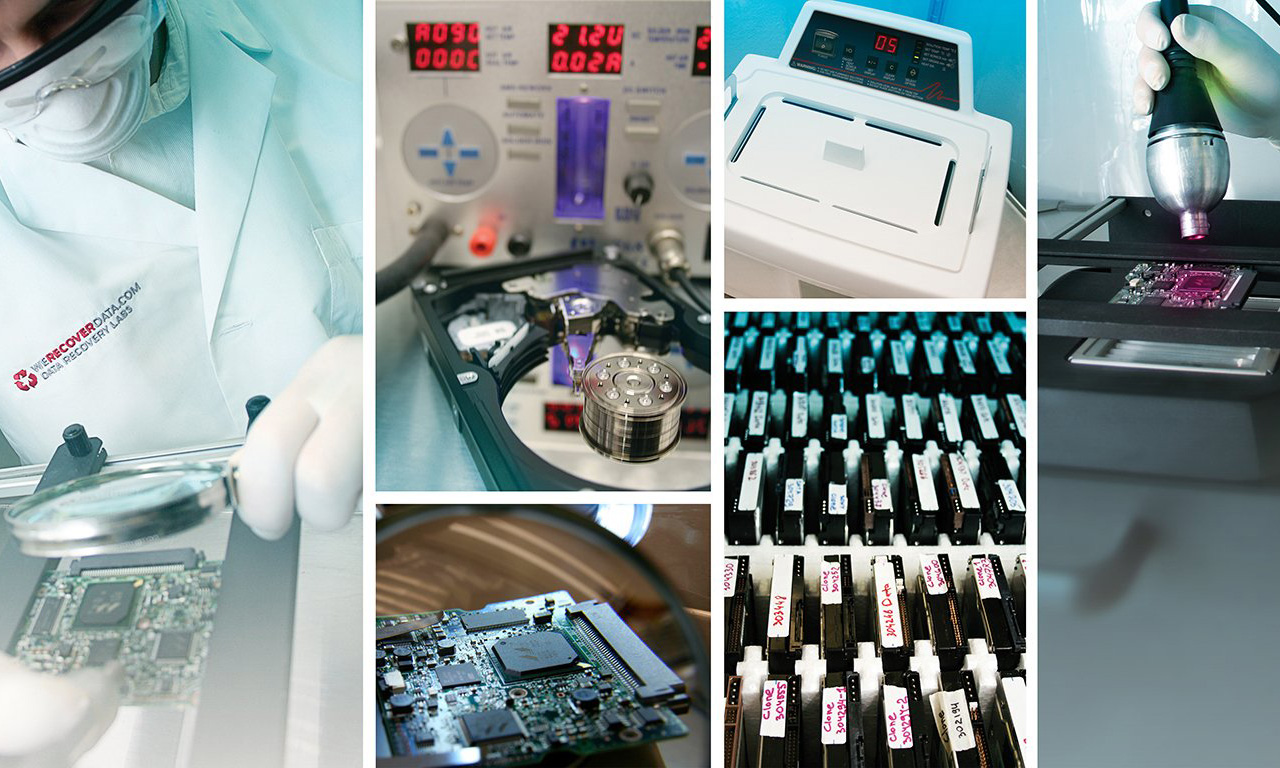
WeRecoverData.com® – Data Recovery Labs has extensive experience with RAID Data Recovery from RAID, spanned and striped systems.
- In most instances, we require only the storage device in order to retrieve the lost data.
- Human error causes most RAID failure, no matter how well designed or implemented the system is.
- Mistakes are easy to make. The more complex the system is, the more potential there is for error.
- We are able to process an array as a collection of image files, enabling fast and easy RAID Data Recovery.
- Our Data Recovery systems have the capacity to absorb most server array volumes.
- Recover RAID with the industry leading RAID Data Recovery provider.
TIP: How to choose the right company to perform RAID data recovery service?
If a company asks for the RAID controller, do not use them.
The RAID Controller is not required to perform the recovery if the company that is attempting the recovery knows enough about RAID systems.
When a customer is sending the equipment to a data recovery company, most companies who claim to perform RAID recoveries will require the RAID controller. That means that they do not have the capabilities to do the recovery without the controller or don’t have the knowledge to perform an advanced recovery from the array.
They will most likely need the RAID Controller to identify the parity information or to use the controller to try rebuilding the array. These are simple steps that only work for very limited types of cases. This process can potentially damage the success of any future recovery, if done wrong. Also in most cases this attempt will not be successful due to drive corruption, which is the most common reason for arrays to fail in the first place.
We receive a large number of cases from customers who sent RAID arrays to other companies to attempt a recovery, and in many of them the data is lost forever due to failed recovery attempts.
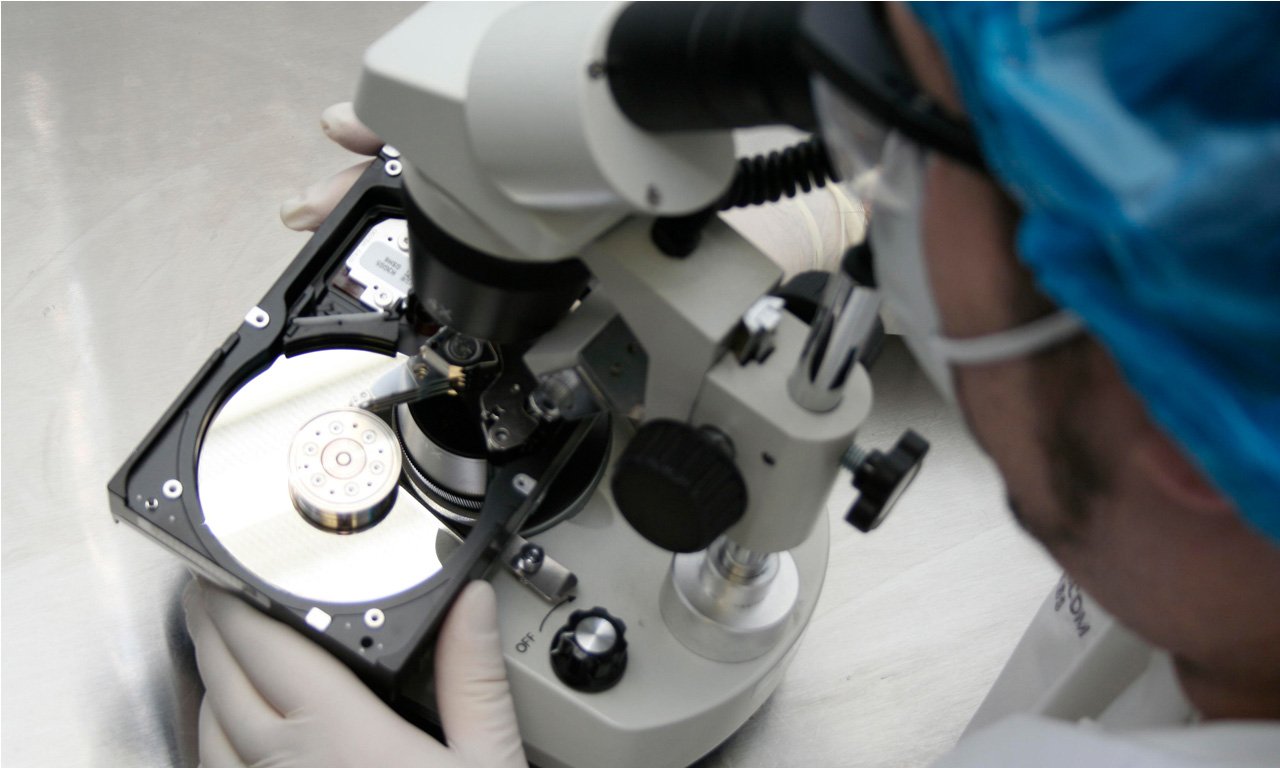
Advanced knowledge and experience with file system formats at the sector level is critical for all recoveries. Understanding the HEX/Binary format at the lowest level that exists in file systems in general, and in particular for RAID arrays, is essential to the success of the recovery. The vast knowledge we have help us recover NAS or complex SAN devices which are using non-standard, proprietary or modified file systems .
See examples of our developments here:
https://www.reuters.com/article/2009/08/03/idUS117072+03-Aug-2009+PRN20090803
https://www.prnewswire.com/news-releases/werecoverdatacom-extends-enterprise-data-recovery-expertise-to-hp-lefthand-storage-access-networks-62227652.html
RAID Data Recovery Testimonials
„All our data is fully restored, and we’re back to normal. Thanks so much for saving our business!
We were in the middle of changing our office domain, and our main file server went down, evidently a physically damaged RAID. Then we discovered that the tape backup had not been functioning properly, so we’d lost about 5 month’s work. One of the things the disc had contained was a huge database for our major client (The Coca-Cola Company ![]() ) , and it was almost time to deliver it to them. If we couldn’t get our data back we would almost certainly go out of business.
) , and it was almost time to deliver it to them. If we couldn’t get our data back we would almost certainly go out of business.
We called the lab and took the server in for data recovery. They worked on it for over a week, and in the end recovered all the lost data. Needless to say, we have everything double backed-up now. ”
Simon Hinkler
VidiPax NYC
![]()
RAID FAQs
Q: We re-striped/re-initialized the RAID array, formatted the array and copied data back to it. Is there a chance of recovering the data from before the array was re-striped/re-initialized?
A: It’s still possible to recover the data on these cases. It will depend on the RAID controller’s functionality and how much data was copied to the array. Contact us to determine how we can help you in your RAID data recovery process.
Q: 2 drives we down and are not recognized by the system in our RAID 5 system, can you still recovery it?
A: It’s still possible to recover the data on these cases. We will have to create clones of the original drives with our equipment after disassembling the drives in the clean room. Then with the clones we will rebuild the RAID array using our proprietary procedure. Please send us all drives that were used in the RAID system, we will need all of them to recover the data.
RAID (Technical Information)
(rād) Short for Redundant Array of Independent (or Inexpensive) Disks, a category of disk drives that employ two or more drives in combination for fault tolerance and performance.
There are a number of different RAID levels:
Standard RAID Level
RAID Level 0
Striped Disk Array without Fault Tolerance: Provides data striping (spreading out blocks of each file across multiple disk drives) without redundancy. This improves performance but does not deliver fault tolerance. If one drive fails then all data in the array is lost.
RAID Level 1
Mirroring and Duplexing: Provides disk mirroring. Level 1 provides twice the read transaction rate of single disks and the same write transaction rate as single disks.
RAID Level 2
Error-Correcting Coding: Not a typical implementation and rarely used, Level 2 stripes data at the bit level rather than the block level.
RAID Level 3
Bit-Interleaved Parity: Provides byte-level striping with a dedicated parity disk. Level 3, which cannot service simultaneous multiple requests, also is rarely used.
RAID Level 4
Dedicated Parity Drive: A commonly used implementation of RAID, Level 4 provides block-level striping (like Level 0) with a parity disk. If a data disk fails, the parity data is used to create a replacement disk. A disadvantage to Level 4 is that the parity disk can create write bottlenecks.
RAID Level 5
Block Interleaved Distributed Parity: Provides data striping at the byte level and also stripe error correction information. This results in excellent performance and good fault tolerance. Level 5 is one of the most popular implementations of RAID.
RAID Level 6
Independent Data Disks with Double Parity: Provides block-level striping with parity data distributed across all disks.
RAID Level 0+1
A Mirror of Stripes: Not one of the original RAID levels, two RAID 0 stripes are created, and a RAID 1 mirror is created over them. Used for both replicating and sharing data among disks.
RAID Level 10
A Stripe of Mirrors: Not one of the original RAID levels, multiple RAID 1 mirrors are created, and a RAID 0 stripe is created over these.
RAID Level 7
A trademark of Storage Computer Corporation that adds caching to Levels 3 or 4.
Nested RAID levels
That configuration provides redundancy is typically combined with RAID 0 to achieve better read/write performance.
RAID 0+1
RAID 1 + 0
RAID 100 (RAID 1+0+0)
RAID 0+3 and 3+0
RAID 0+3
RAID 30
RAID 50 (RAID 5+0)
RAID 51
RAID 05 (RAID 0+5)
RAID 53
RAID 60 (RAID 6+0)
Non-standard RAID structure we can recover data from
RAID S
EMC Corporation’s proprietary striped parity RAID system used in its Symmetrix storage systems.
| Traditional RAID 5 | EMC RAID S | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
Others:
Double parity
RAID-DP
RAID 1.5
RAID 5E, RAID 5EE and RAID 6E
Parity RAID
Intel Rapid Storage Technology (formerly called Intel Matrix RAID)
Linux MD RAID 10
RAID 1E
RAID-K
RAID-Z
RAID-Z2
Tahoe Distributed File System
Drive Extender
BeyondRAID
UnRAID
Drobo BeyondRAID
We practically support any type of RAID level format due to our capabilities.




















Great company!
I think it is the best company in the world regarding data recovery. They take all types of recovery cases with great responsibility and ensure they work with the best possible solution for your specific case. I highly recommend it.
Superb effort
Superb effort from werecoverdata. I had no idea how to fix it when I faced a horrible problem with my RAID NAS. But they solved it very quickly and superbly. I recommend them!
Fantastic results
Thanks to all staff of werecoverdata for excellent work and for getting my company data back! I got frustrated when a deadly drop damaged my hard drive. But they solved it!
Thanks
Few days ago my raid server is crashed dangerously. It was not starting any more. I tried in a various way whatever I know but I could not fix it. My uncle told me about WeRecoverdata. Then contact with them and they repaired it. Thank you guys.
Recover service
Those are suffering bad experience of getting a reliable and professional recovery service provider, definitely, they can choose werecoverdata. I highly recommend it.
Thanks a lot
The location is a bit hard to find out but eventually, I did. They recovered my hard drive, which was mostly dead. Thanks a lot.
Great response
Definitely weRecover team is great to solve that kind of hard drive problem. Great response and remarkable. They recovered my all data successfully within short time. I wanna give special thank to David. Thanks a lot man.
Liked Your Service
I have been using my HP laptop since 2016. Few months ago I could not open my laptop. After pressing the power button its showing nothing. My friend told me about that company. They recovered my laptop. Now its working perfectly. Thanks a lot WeRecoverData.
Pretty good experience
It was really pretty good experience. They are so professional, punctual and reliable. I strongly recommend it.
Remarkable Work
A lot of thanks to werecoverdata. You did really remarkable work. I was frustrated when lost my important data from a hard drive. I sent my hard drive to WRD then they got all the data back. At first, I couldn’t believe anyone can recover it since my computer tech said he can’t do it. All credit goes to werecoverdata.
Gorgeous service
Fantastic service from all the guys at werecoverdata. I was having pressure when corrupted data from my hard drive .Then I went there and they fixed it superbly.Thanks for removing the pressure!
Extremely well
I faced horrible problem but they solved it extremely well.My problem was that hard drive crashed dangerously.At this moment I thought the sky was broken on my head.Thank you for that.
Sensible
Thanks to WeRecoverData. You fixed the hard drive problem promptly. I am impressed… Anybody can rely on werecoverdata.
Well done
Thank you
Great work
Obviously great work from werecoverdata.Definitely no doubt about this company because they take seriously to solve any kinds of problem.I have lot of assurance at them.A lot of thanks to them.
Fantastic work
Oh Tom really fantastic work. You saved my important days. Raid 5 server damaged dangerously few days ago. But you fixed it well. Thank you for that!
Great efforts
All credits goes to werecoverdata for recovering raid server.I thought impossible to repair it but they was taken sensible and fixed it.Now I can fully trust on werecoverdata.All thanks to them.
Helpful Work
Werecoverdata, you did a really very helpful work.I was angry when my hard drive got dropped from my mistakes. I recommend the company and give a lot of thanks to werecoverdata.
Best service
After my hard drive crashed I was going to be totally mad. One of mu cousin suggested me to meet that company. I did and got the best service ever I had.
Remarkable Job
AWESOME service from WeRecoverData. I was almost mad when my pc crashed. A lot of valuable data in my hard drive. One of my friend recommend it. I thought it will not be possible.
But after all I got back my all data. Thank You WeRecoverData.